Circumcision is performed for religious, cultural, or health reasons and is known to offer various health benefits. While it is typically performed in infancy, circumcision can also be done during childhood, adolescence, and adulthood.
Circumcision involves the surgical removal of the foreskin, known as the prepuce, from the penis. This procedure is widely performed worldwide for cultural, religious, and health reasons. Circumcision facilitates penile hygiene, reduces the risk of urinary tract infections, and provides protection against sexually transmitted infections.
The primary purpose of circumcision is to enhance penile hygiene and prevent certain health issues. In circumcised males, the head of the penis (glans) remains exposed, making it easier to maintain cleanliness. Additionally, circumcision lowers the risk of urinary tract infections, balanitis (inflammation of the glans), and sexually transmitted infections.
For children, the recommended age for circumcision is generally before 18 months or after six years. The period before 18 months is often when children have no memory of the procedure. Children older than six years can understand and consent to the procedure.
When performed within these age ranges, circumcision is unlikely to cause any psychological issues later in life. It is recommended that circumcision surgeries be performed in fully equipped hospitals.
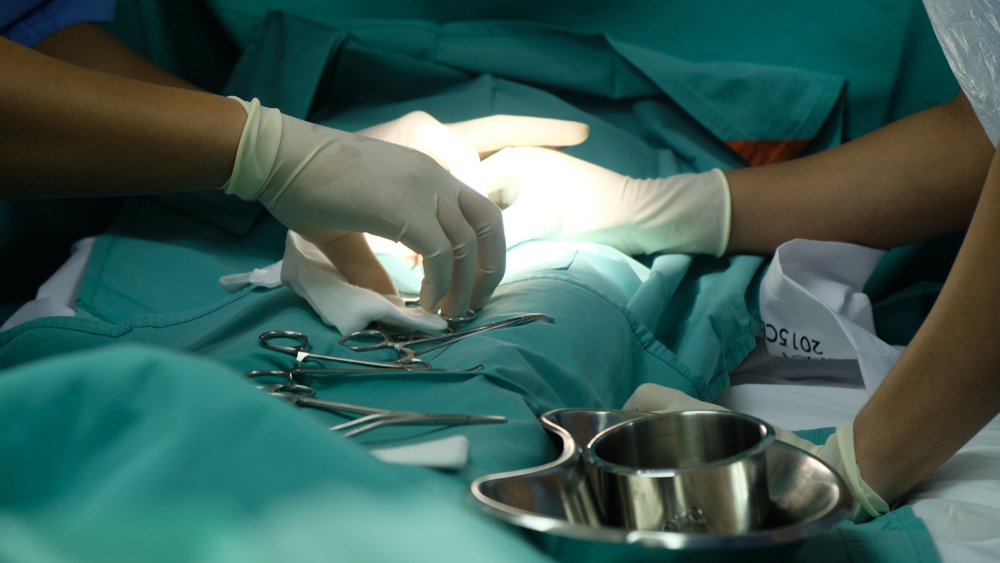
Circumcision surgery is typically performed under local anaesthesia or light sedation. In infants, local anaesthesia can be used for a quick and simple procedure, while older children and adults may require light sedation or general anaesthesia. During the procedure, the surgeon cuts and removes the foreskin (prepuce) and then closes the incision with surgical stitches or adhesive.
The procedure usually takes 15-30 minutes, and the patient is typically discharged the same day. After circumcision, mild swelling, redness, and sensitivity in the penis are normal and generally resolve within a few days. It is important to adhere to hygiene rules and follow the care instructions provided by the surgeon during the recovery period.
Circumcision offers numerous health benefits. Circumcised males have a lower risk of urinary tract infections, and maintaining penile hygiene is easier. Additionally, circumcision can reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), HIV, and HPV. Circumcised males are also less likely to develop balanitis and other penile infections. These health benefits are among the reasons why circumcision is widely practiced globally.
However, there are known risks and complications associated with circumcision. Postoperative complications may include infection, bleeding, and wound healing issues. Additionally, although rare, surgical errors can cause damage to penile tissue. The benefits and risks of circumcision should be thoroughly discussed with a doctor before the procedure, allowing parents to make an informed decision at the appropriate time.
After circumcision surgery, it is important for patients to closely monitor their symptoms and follow their doctor's instructions. Mild swelling, redness, and sensitivity are normal after the procedure but typically resolve within a few days. Parents should ensure that the wound area remains clean and dry, adhering to hygiene rules.
Additionally, taking prescribed pain relievers and antibiotics regularly can reduce the risk of infection and speed up the healing process. Regular follow-up appointments with the doctor are crucial to assess wound healing and monitor for potential complications. This care and follow-up process helps ensure a healthy recovery and allows for the long-term health benefits of circumcision. For detailed information, contact EMPCLINICS.
Typically, no special tests are needed for children. However, adults may require preoperative blood tests and health assessments before the surgery.
The procedure is performed under anaesthesia, so no pain is felt during surgery. Mild pain, discomfort, and swelling may occur after surgery, but these can be easily managed with medication prescribed by the doctor.
Mild bleeding and oozing are normal, but heavy or prolonged bleeding requires immediate medical attention.